-
About UsZHONGTAI HENGBANG Engineering Technology Co., Ltd. is located in the Academician Entrepreneurship Base of Tai'an National High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, Shandong Province. The company is a comprehensive service provider specializing in engineering consulting and design, materials R&D and manufacturing, as well as operations and maintenance. With strong technical expertise and robust R&D capabilities, its products are primarily applied in critical areas such as water conservancy infrastructure projects, transportation infrastructure initiatives, and environmental protection solutions for isolating and preventing leakage from urban waste and highly hazardous industrial solid waste.

-
ProductsZHONGTAI HENGBANG Engineering Technology Co., Ltd. boasts production lines sourced from countries including Germany, Italy, Denmark, Belgium, and Switzerland, adhering to rigorous quality management systems and testing standards. We are equipped with advanced testing equipment capable of evaluating tensile strength, creep resistance, UV protection, water permeability, flame retardancy, antistatic properties, chemical corrosion resistance, and oxidation performance.

-
Application CasesThe product is primarily used in hydraulic infrastructure projects, transportation infrastructure projects, and environmental protection applications—including the isolation and impermeability of municipal waste and highly hazardous industrial solid waste.

-
BlogPrioritizing technological advancement and innovation, our company is committed to fulfilling user needs to the fullest extent possible.
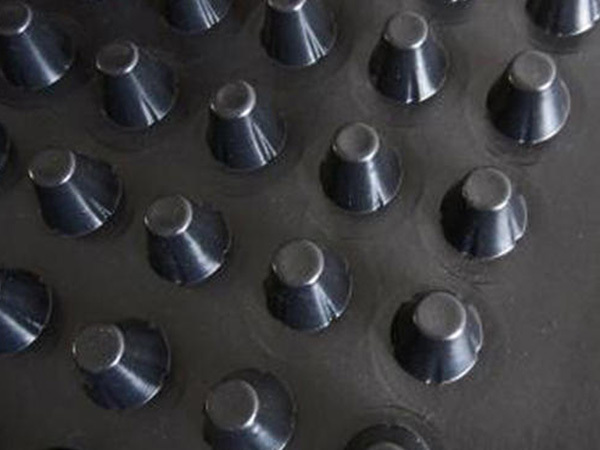
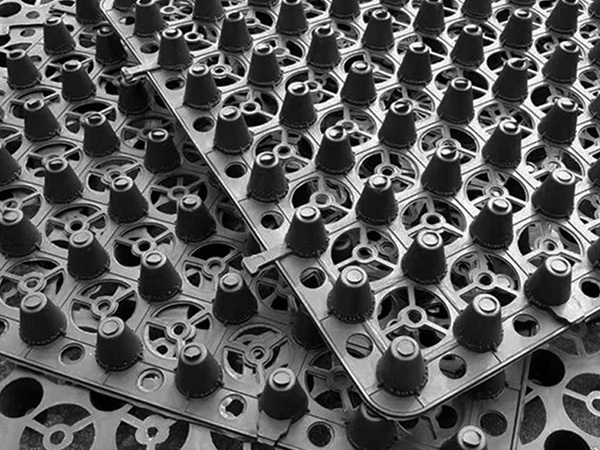
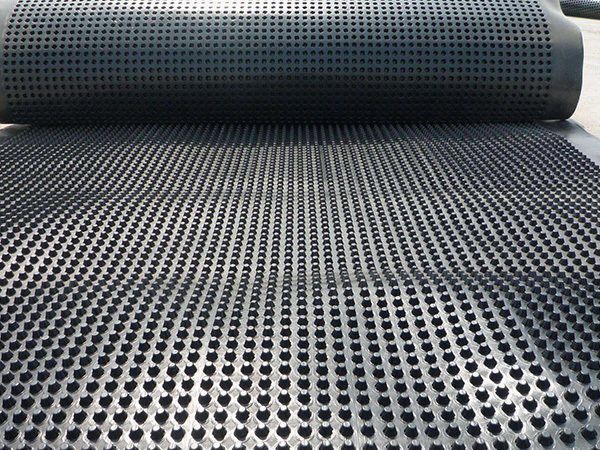


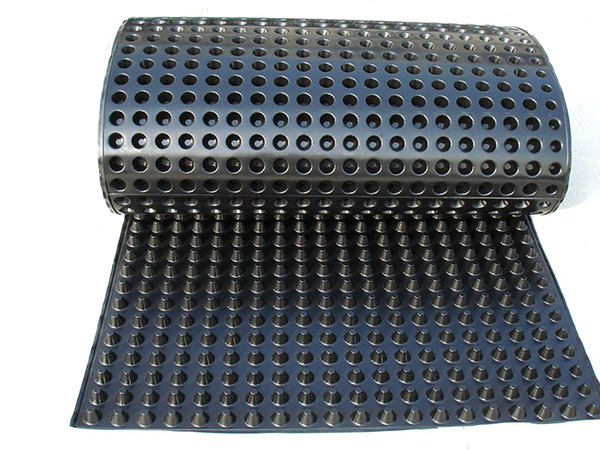




Plastic drainage board
Plastic drainage boards, also known as plastic drainage strips, come in various shapes, including wavy and accordion-like designs. At their core is an extruded plastic core board, which serves as the structural backbone and primary drainage channel. This core features a parallel cross-sectional design, with both sides wrapped in non-woven geotextiles that act as filtration layers. The core provides essential support while simultaneously directing water absorbed by the filter layers upward and out of the system. As a result, these drainage strips offer an ideal vertical pathway for effective drainage consolidation in saturated cohesive soils such as silts, clayey soils, and fill materials—significantly reducing the time required for soft soil stabilization and consolidation.
Keywords:
Detailed description
Product Introduction:
Plastic drainage boards, also known as plastic drainage strips, come in various shapes, including wavy and accordion-like designs. At their core is an extruded plastic core board, which serves as the structural backbone and primary drainage channel. This core features a parallel cross-sectional design, with both sides encased in non-woven geotextiles that act as filtration layers. The core itself provides essential support while simultaneously channeling water that has seeped through the filter layers upward. As a result, these drainage strips create efficient vertical pathways for dewatering and consolidation processes, making them ideal for treating soft foundations composed of saturated cohesive soils such as silts, clays, and fill materials—significantly reducing the time required for soft soil consolidation.
Main applications:
Landscape Engineering: Garage Roof Greening, Rooftop Gardens, Football Fields, Golf Courses.
Municipal Engineering: Road Subgrades, Subway Tunnels.
Construction Engineering: Upper or lower layers of building foundations, interior and exterior walls of basements, as well as roof waterproofing and insulation layers.
Transportation Engineering: Highways, railway subgrades, embankments, and protective layers.
Get a product quote
We’re here to help you every step of the way! Please fill out our inquiry form, and our team will respond promptly.
Recommended Products
Strong technological capabilities and robust R&D expertise
Laminate Film Machine-Woven Fabric
ZHONGTAI HENGBANG Engineering & Technology Co., Ltd.
Address: East Section of Zhongtianmen Avenue, Tai'an High-tech Zone, Shandong Province
Service Hotline

COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.






